 |
Since 2015, the Friends of Sara Lapi Association has established a Degree Award named after Sara in collaboration with the University of Florence and in particular with the "Ugo Schiff" Department of Chemistry at the Scientific Center of Sesto Fiorentino. This year's award goes to Niccolò Preti for his thesis "Towards dipolar quantum gases in a ring". Well done! more info |
LAST NEWS
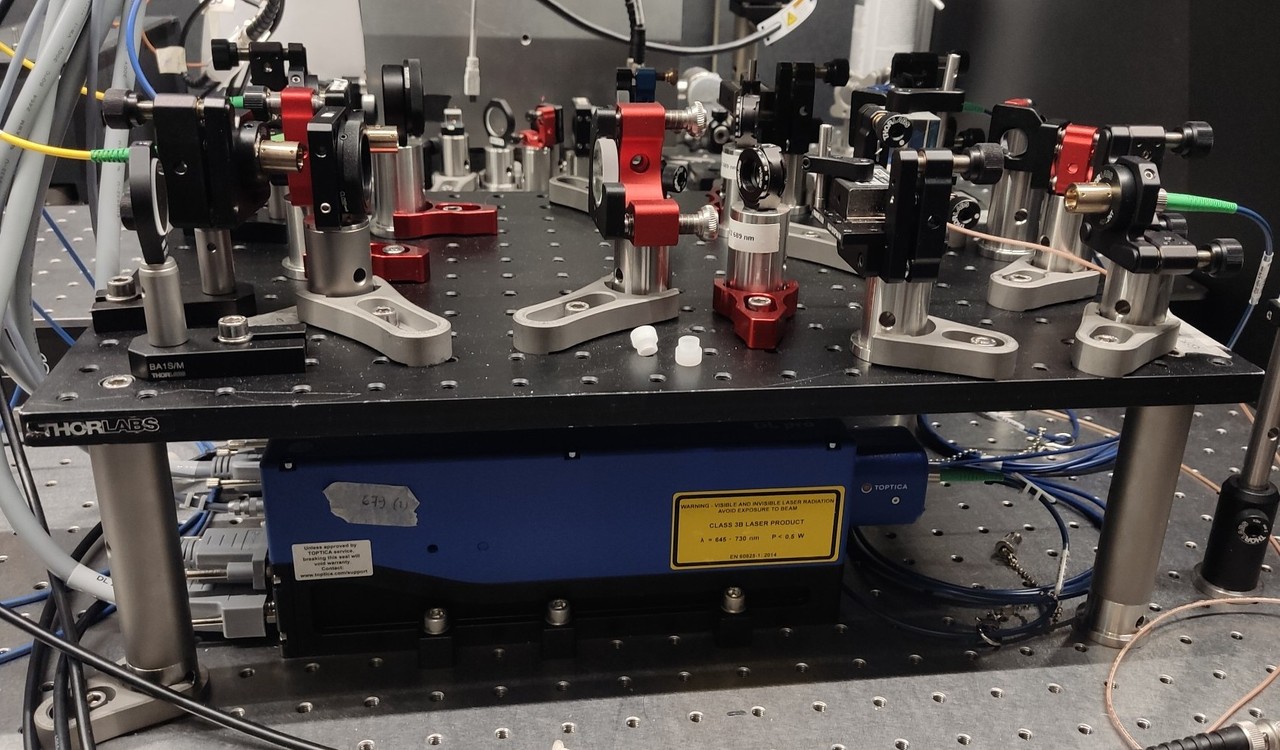 |
We’ve successfully integrated the 679nm and 707nm lasers into our experiment. They improve the blue and red mot stages by closing two decay channels, leading to a factor of 10 increase in density that is helpful to move forward with our optical tweezers. Stay tuned for the next update! |
 |
We are immensely proud of Ludovica Donati, who successfully defended her PhD thesis, “Generating quantum coherence with incoherent radiation”. Her research deals with the production of Fano coherence in atomic systems induced by interactions with incoherent radiation, paving the way for the first detection of such phenomena on this platform. This achievement marks an important milestone in her academic career and we look forward to her future contributions to the scientific community. Congratulations, Dr. Donati! . See also the thesis here |
 |
In this ambitious EIC Transition project we aim at developing the laser of our dreams: narrow and stable everytime you push the ON button. The project is a joint effort between the Ba+/Li group and the companies SILENTSYS, IDIL and A8. They will help us turn our ideas into a real product. We are looking for motivated people to join us, contact us for open positions! |
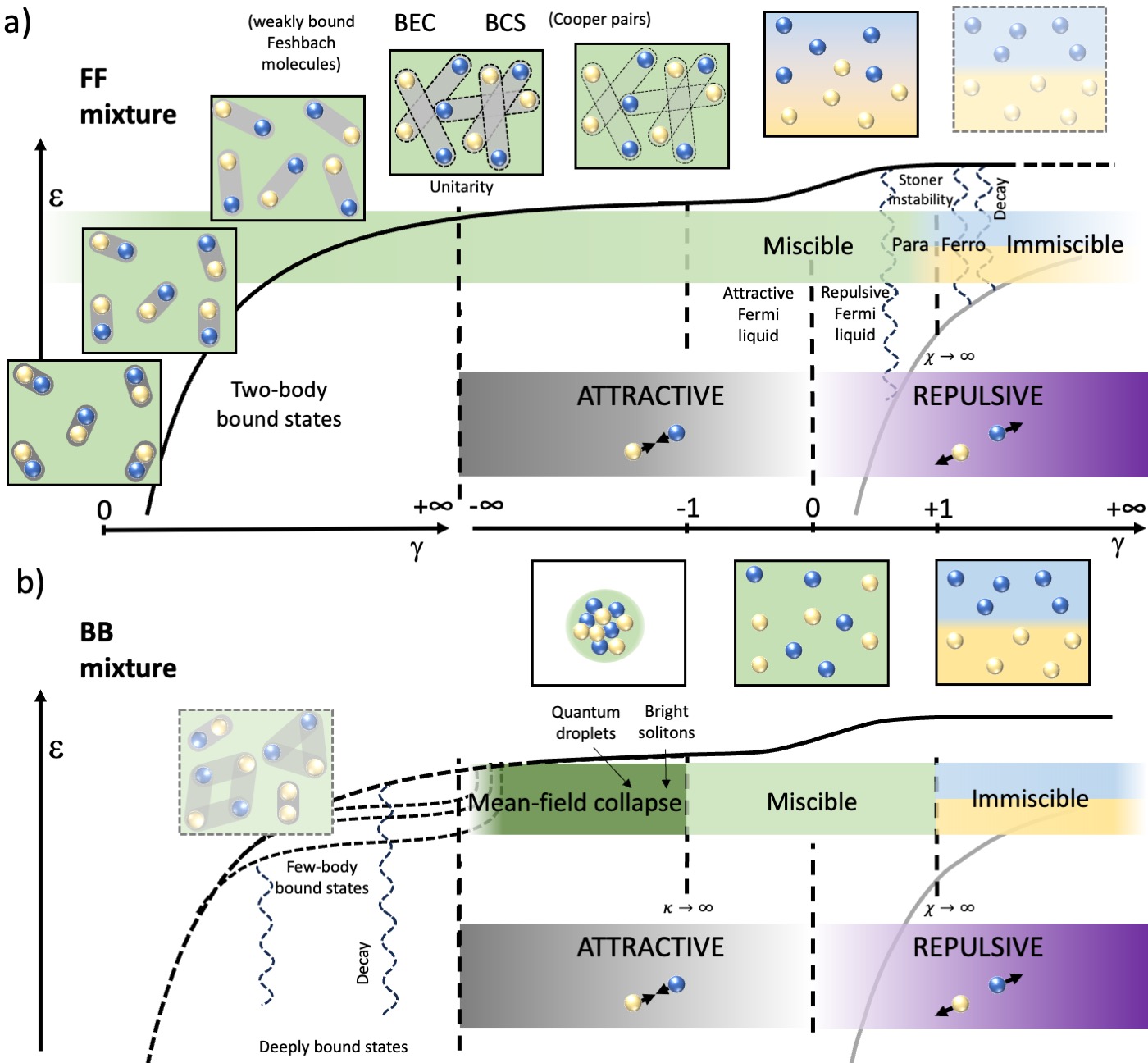 |
After decades of improvements in cooling techniques of several atomic species and in finding methods to achieve stable quantum mixtures, the field is now ready for an extensive use of such versatile platforms to investigate various physical problems. Relevant examples are the dynamics of impurities in a quantum gas, the miscibility condition of different gases, the study of exotic topological structures, the interplay between magnetism and superfluidity, the formation of artificial molecules or new few-body states. In this review we illustrate the differences among possible quantum mixtures — whether homonuclear spin mixtures or heteronuclear ones — and show how they can be exploited to investigate a plethora of topics from the few-body to the many-body regime. In particular, we discuss quantum mixtures of ultracold gases under three different perspectives: systems made of a few atoms of different kinds, single impurities within a host gas and quantum mixtures of two interacting gases. C. Baroni et al. |
