 |
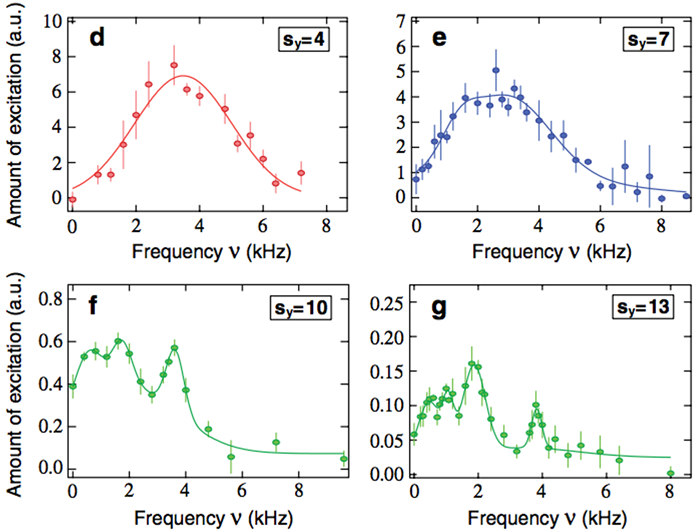
We report the Bragg spectroscopy of interacting one-dimensional Bose gases loaded in an optical lattice across the superfluid to the Mott-insulator phase transition. Elementary excitations are created with a nonzero momentum and the response of the correlated 1D gases is in the linear regime. The complexity of the strongly correlated quantum phases is directly displayed in the spectra which exhibit novel features. This work paves the way for a precise characterization of the state of correlated gases in optical lattices. D. Clément et al., See also the Physics Viewpoint by D. Jaksch: D. Jaksch |
LAST NEWS
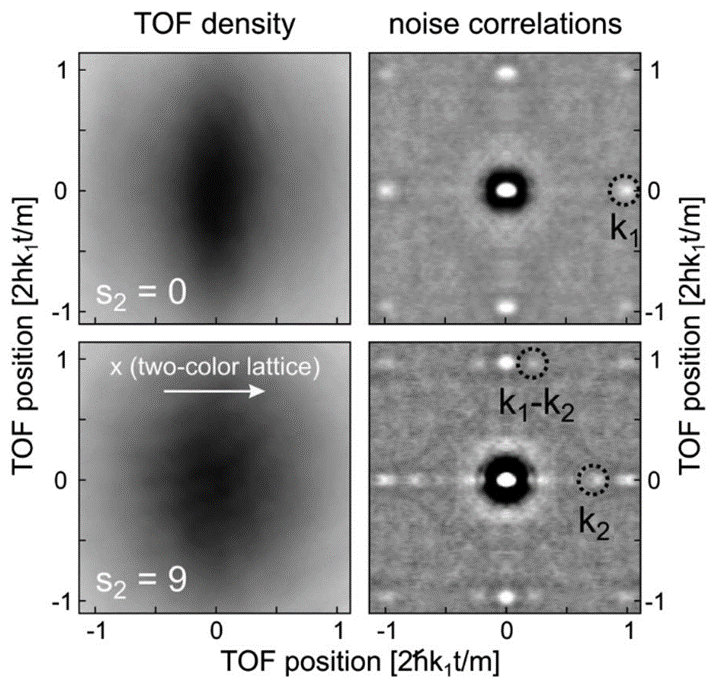 |
We use a two-color lattice to break the homogeneous site occupation of an atomic Mott insulator of bosonic 87Rb. We detect the disruption of the ordered Mott domains via noise correlation analysis of the atomic density distribution after time of flight. The appearance of additional correlation peaks evidences the redistribution of the atoms into a strongly inhomogeneous insulating state, in quantitative agreement with the predictions. V. Guarrera et al. |
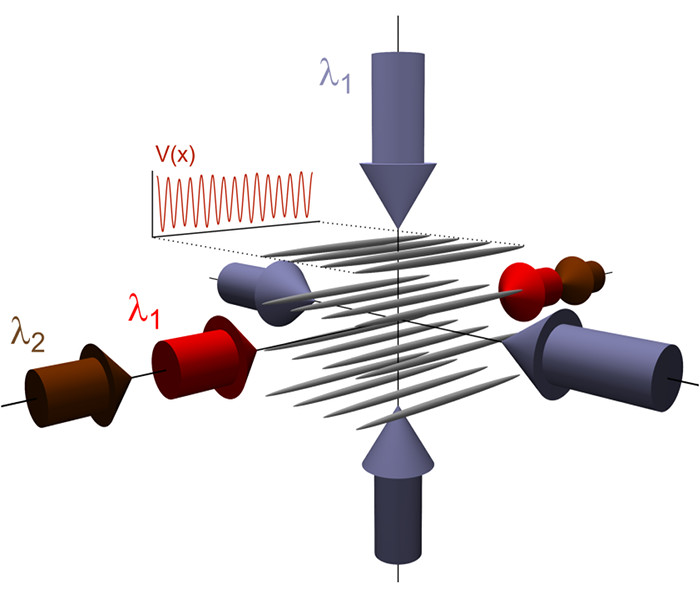 |
We use a bichromatic optical lattice to experimentally realize a disordered system of ultracold strongly interacting 87Rb bosons. In the absence of disorder, the atoms are pinned by repulsive interactions in the sites of an ideal optical crystal, forming one-dimensional Mott-insulator states. We measure the excitation spectrum of the system as a function of disorder strength and characterize its phase-coherence properties with a time-of-flight technique. Increasing disorder, we observe a broadening of the Mott-insulator resonances and the transition to a state with vanishing long-range phase coherence and a flat density of excitations, which suggest the formation of a Bose-glass phase. L. Fallani et al. |
 |
We have performed pioneering investigations of a Bose-Einstein condensate in a random potential, produced by shining an optical speckle pattern onto the atoms. We have investigated both static and dynamic properties of the BEC in the presence of disorder. With small levels of disorder, stripes are observed in the expanded density profile and strong damping of dipole and quadrupole oscillations is seen. By studying the propagation of the BEC in a disordered waveguide, we have evidenced a strong suppression of mass transport as the speckle potential is increased. The experimental results are in good agreement with numerical calculations based on the Gross-Pitaevskii equation. J. E. Lye et al. C. Fort et al. |
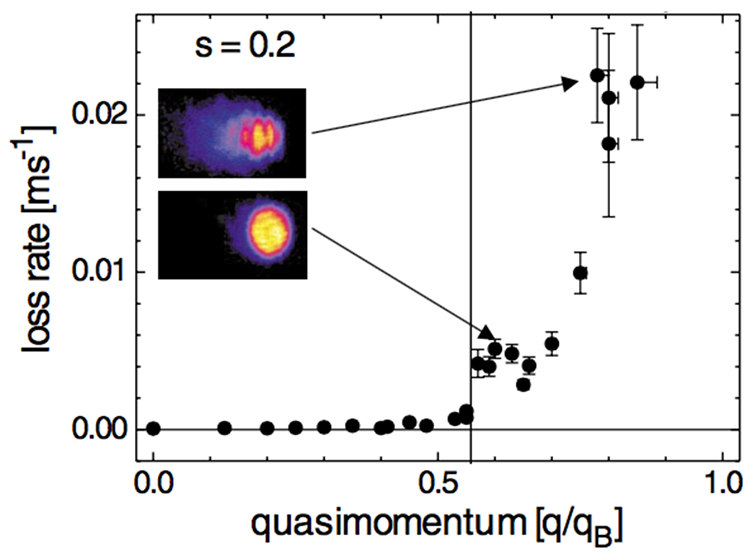 |
We have experimentally studied the unstable dynamics of a harmonically trapped Bose-Einstein condensate loaded into a 1D moving optical lattice. The lifetime of the condensate in such a potential exhibits a dramatic dependence on the quasimomentum state. This is unambiguously attributed to the onset of dynamical instability, after a comparison with the predictions of the Gross-Pitaevskii theory. Deeply in the unstable region we observe the rapid appearance of complex structures in the atomic density profile, as a consequence of the condensate phase uniformity breakdown. L. Fallani et al. |
