 |
Quantum phase slips, i.e., the primary excitations in one-dimensional superfluids at low temperature, have been well characterized in most condensed-matter systems, with the notable exception of ultracold quantum gases. Here we present our experimental investigation of the dissipation in one-dimensional Bose superfluids flowing along a periodic potential, which show signatures of the presence of quantum phase slips. In particular, by controlling the velocity of the superfluid and the interaction between the bosons we are apparently able to drive a crossover from a regime of thermal phase slips into a regime of quantum phase slips. Achieving a good control of quantum phase slips in ultracold quantum gases requires to keep under control other phenomena such as the breaking of superfluidity at the critical velocity or the appearance of a Mott insulator in the strongly correlated regime. Here we show our current results in these directions. S. Scaffidi Abbate, et al., |
LAST NEWS
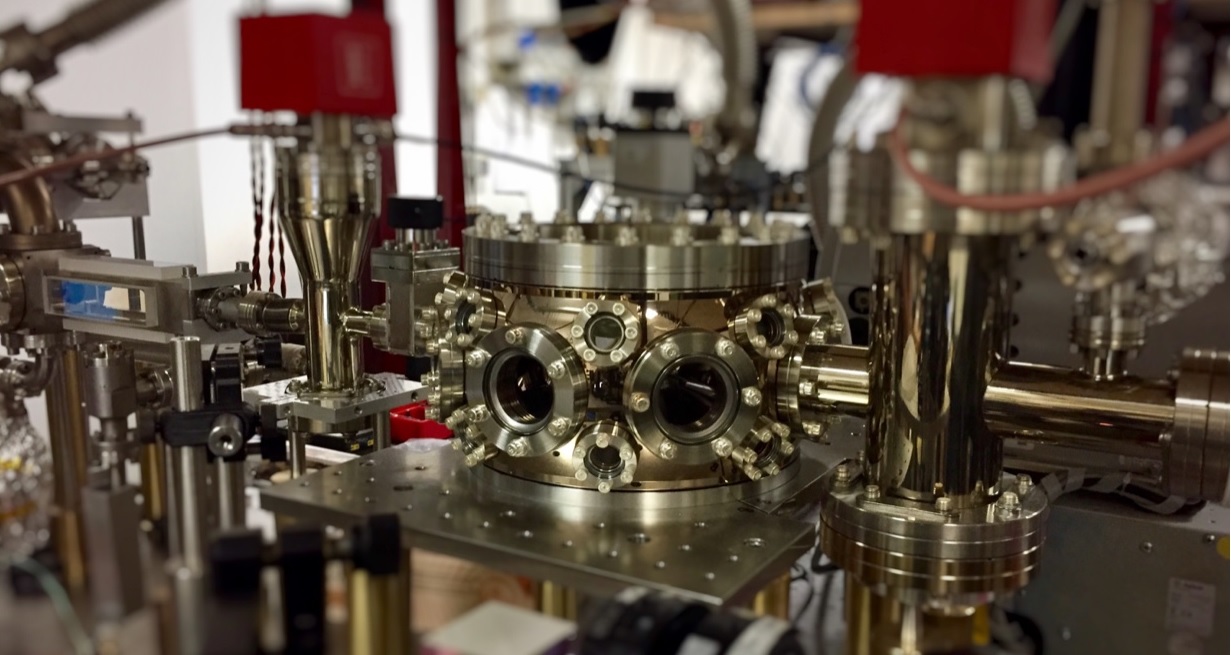 |
We assembled a new vacuum system: a single 2D MOT for both the 87Rb and 41K plus a 3D MOT where we plan to produce a “dimple trap” for the evaporation of the double species condensate. The chamber is provided with re-entrant viewports for high resolution optical access. |
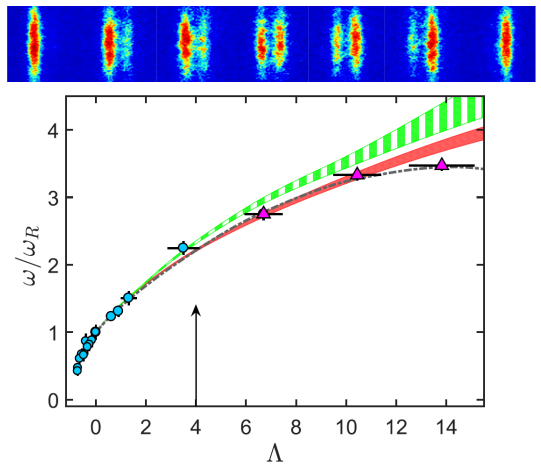 |
We explore the interplay between tunneling and interatomic interactions in the dynamics of a bosonic Josephson junction. We tune the scattering length of an atomic K39 Bose-Einstein condensate confined in a double-well trap to investigate regimes inaccessible to other superconducting or superfluid systems. In the limit of small-amplitude oscillations, we study the transition from Rabi to plasma oscillations by crossing over from attractive to repulsive interatomic interactions. We observe a critical slowing down in the oscillation frequency by increasing the strength of an attractive interaction up to the point of a quantum phase transition. With sufficiently large initial oscillation amplitude and repulsive interactions, the system enters the macroscopic quantum self-trapping regime, where we observe coherent undamped oscillations with a self-sustained average imbalance of the relative well population. The exquisite agreement between theory and experiments enables the observation of a broad range of many body coherent dynamical regimes driven by tunable tunneling energy, interactions and external forces, with applications spanning from atomtronics to quantum metrology. G. Spagnolli, et al., |
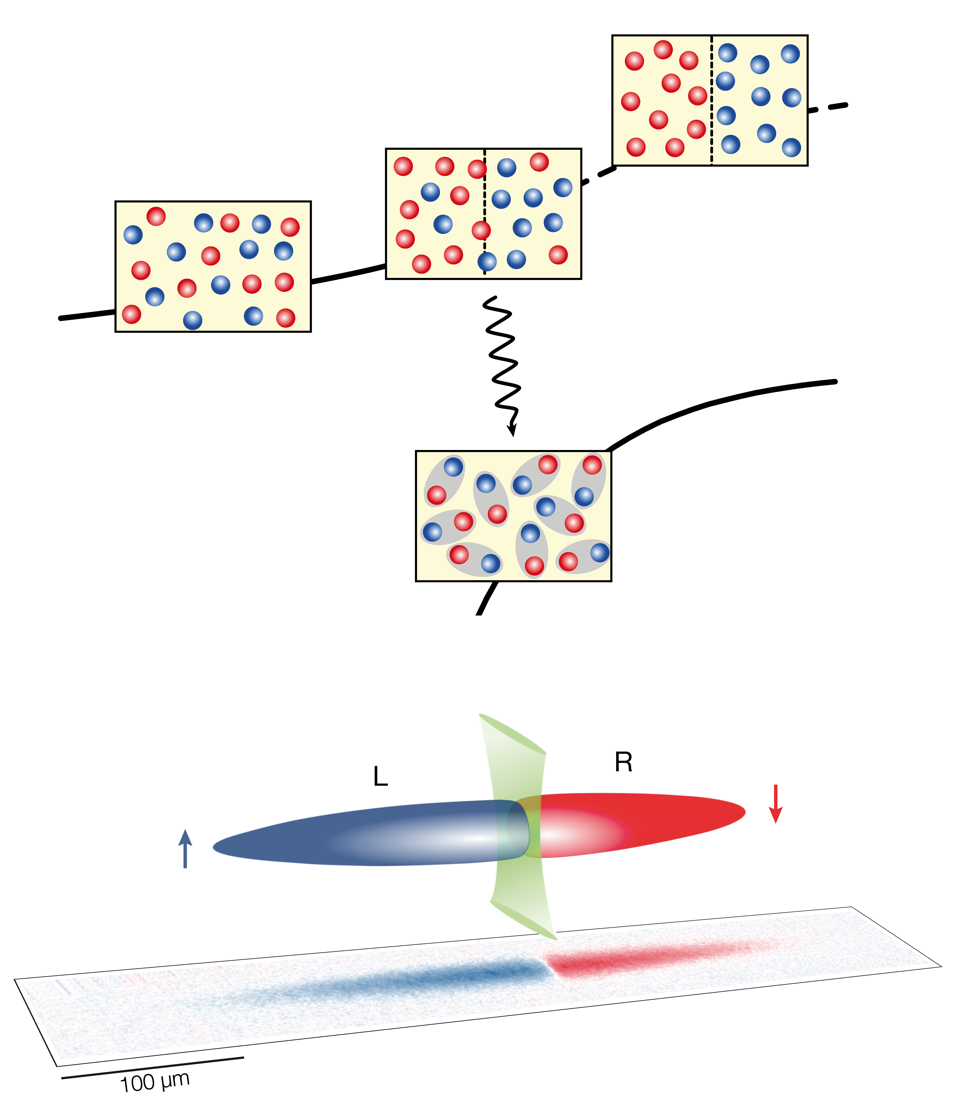 |
We study the collective spin response and spin diffusion of an ultracold lithium Fermi gas artificially engineered in a fully ferromagnetic state, obtained by spatially segregating oppositely-oriented spins into two adjacent reservoirs. In this way, we show that strong repulsive interactions are sufficient to temporarily stabilize ferromagnetic correlations in a Fermi mixture. In particular, we reveal a substantial increase of the magnetic susceptibility of the gas while approaching the critical value of interaction. Correspondingly, we show that above the critical interaction a spin up-down domain wall can persist for a finite time, indicating the metastability of the ferromagnetic state. Such findings point to Stoner-like ferromagnetic instability driven only by short-range repulsion, and are consistent with our recent study of a repulsive Fermi liquid of polarons in strongly polarized Fermi gases. G. Valtolina, et al., |
 |
We are pleased to announce the workshop of the EU project QUIC (Quantum Simulations of Insulators and Conductors) which will take place at LENS on April, 20th and 21st. The talks will be open and there will be time for lab visits and scientific discussions for everyone interested, not only for the QUIC team members. A detailed program of event can be found here |
